

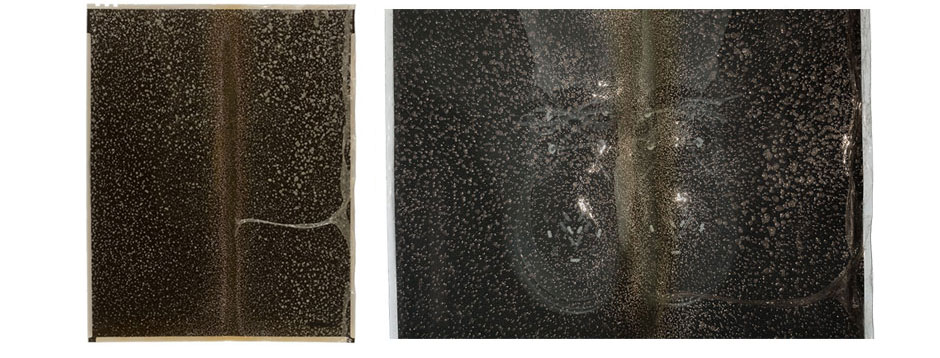
(Left) Acetate sheet film contains plasticizers that can exude from the base to the surface of the film in the form of bubbles. Plasticizer exudation is typical of advanced acetate decay. (Right) The detail of the image on the left shows bubbling plasticizer and discoloration of the film, likely caused by contaminants from an acidic paper enclosure such a seamed envelope.
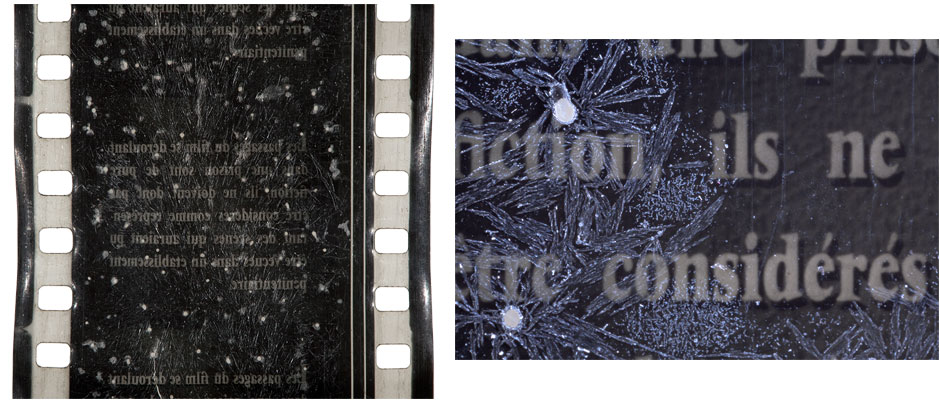

(Left) 35mm film frame with crystallized plasticizer exudation caused by advanced acetate decay. Triphenyl phosphate, a common plasticizer, forms crystals like these when it exudes. (Right) This detail of the image on the left shows the crystalline structure of the plasticizer. Triphenyl phosphate, a common plasticizer, forms crystals like these when it exudes.
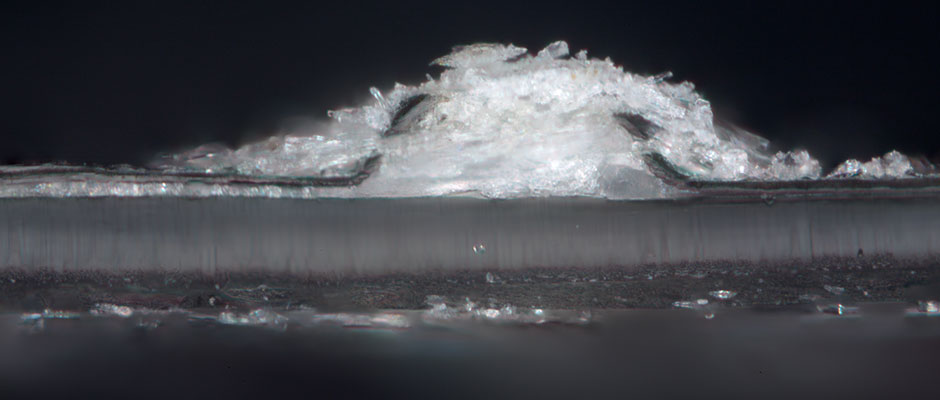
A cross section of the previous image viewed under magnification shows the way the plasticizer pierces through the surface of the gelatin.
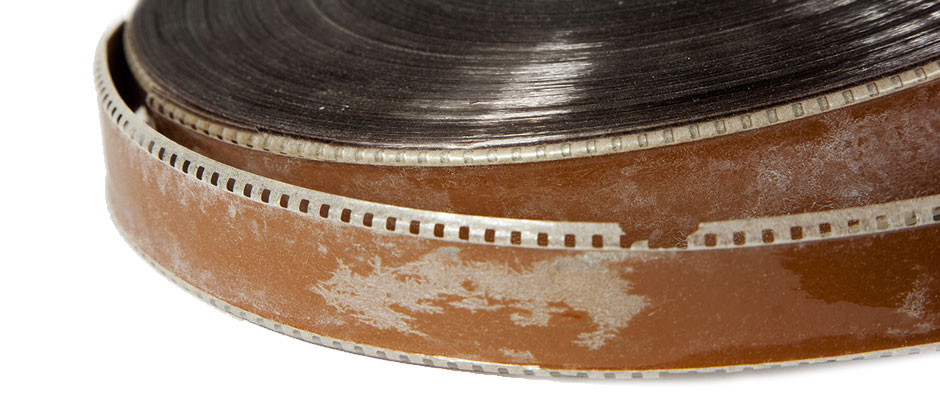

This 35mm full-coat magnetic track is in an advanced state of acetate base decay. Here you can discern the crystalline plasticizer deposits and the brittleness of the film.

The plasticizer bubbles seen here, common in sheet film, are formed by phthalate plasticizers.
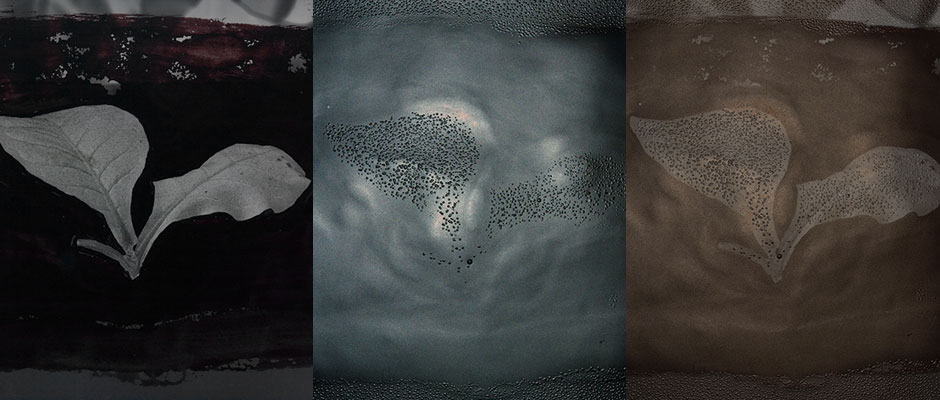
A 5x7 acetate negative, viewed emulsion-side up, shows plasticizer exudation. Masking in the form of opaque paint was applied directly to the negative on the base of the film. This masking prevented the appearance of plasticizer exudation as the acetate base decayed. Elsewhere in the negative the plasticizer bubbles are clearly visible. The negative is photographed in transmitted light (Left), axial light (Center), and raking light (Right).

(Left) Plasticizer has migrated in the 35mm acetate support and formed crystal web-like structures. This example of plasticizer exudation was achieved by subjecting the sample to an accelerated aging test. (Right) In this detail of the previous image, the crystal plasticizer structure can be more clearly discerned. This example of plasticizer exudation was achieved by subjecting the sample to an accelerated aging test.
What it is and what causes itPlasticizer additives are distributed throughout cellulose film bases. Phthalate and triphenyl phosphate are two common plasticizers used in the manufacture of acetate film bases. They provide protection against flammability and bolster dimensional stability, and normally make up from 12-15% of the weight of the film.When acetate film decays, the capacity of the base to retain the incorporated plasticizer decreases, and plasticizers can migrate from the base to the surface of the film in the form of crystals or bubbles. Plasticizer exudation in bubble form can be solid or liquid, and crystalline plasticizer exudation may seem to disappear in the presence of heat only to solidify again when the film cools. Plasticizer exudation can occur on both the base and emulsion sides of the film and is associated with the advanced stages of acetate decay. |
What you can doOnce plasticizer exudes to the surface of the film, there is no way to reverse the process. Plasticizer exudation can be prevented, however, if the progression of acetate base decay is arrested by storage of the film in a cold or frozen and moderately dry environment. In cases of advanced acetate decay, freezing is recommended until such time as the film can be duplicated. |
At Risk
|